With the explosion of big data, handling large datasets has become an essential capability for any BI tool. Power BI has adapted well to this demand, providing features that allow data professionals to analyze and visualize billions of rows effectively. In this article, I’ll walk through the technical aspects of how Power BI’s DirectQuery mode and Dynamic M Query Parameters make it possible to handle a dataset with more than 8 billion data points efficiently.
The Challenge of Big Data in Power BI
Handling billions of rows in Power BI can be challenging due to memory limitations and performance considerations. While importing such large datasets would overwhelm the system, DirectQuery mode and Dynamic M Query Parameters allow you to query and work with a manageable subset of the data in real-time, providing a powerful solution without compromising system performance or responsiveness.
1. Using DirectQuery Mode for Big Data Analysis
DirectQuery is a mode in Power BI that does not import data into Power BI’s in-memory storage. Instead, each time you interact with the data in Power BI, it sends a query back to the data source and retrieves only the relevant subset.
Advantages of DirectQuery for Big Data:
- No Memory Overhead: DirectQuery eliminates the need to load massive datasets into Power BI’s memory, enabling smoother operation even with extremely large datasets.
- Real-Time Data Access: Since Power BI directly queries the source, you’re always working with the latest data, which is beneficial for real-time or near-real-time data analysis.
- Scalability: DirectQuery enables scaling to billions of rows since the storage is handled by the database system rather than Power BI’s in-memory model.
However, DirectQuery has some limitations:
- Performance Dependency: Since all data requests go back to the source, query performance is heavily dependent on the underlying database’s response time.
- Limited DAX Functionality: Certain DAX functions that rely on in-memory processing are not available in DirectQuery mode.
To mitigate some of these limitations, Power BI provides Dynamic M Query Parameters, which help filter and control the data retrieved from the source.
2. Optimizing Performance with Dynamic M Query Parameters
Dynamic M Query Parameters extend the flexibility of Power BI’s DirectQuery mode by adding dynamic filter capabilities. This feature is ideal for optimizing big data queries and improving performance.
How Dynamic M Query Parameters Work
Dynamic M Query Parameters allow Power BI model authors to incorporate parameterized filtering directly into the M query that pulls data from the source. When a user interacts with filter options in Power BI, the filter values are applied as SQL parameters, dynamically narrowing down the dataset before it’s retrieved.
Implementation Example of Dynamic M Query Parameters
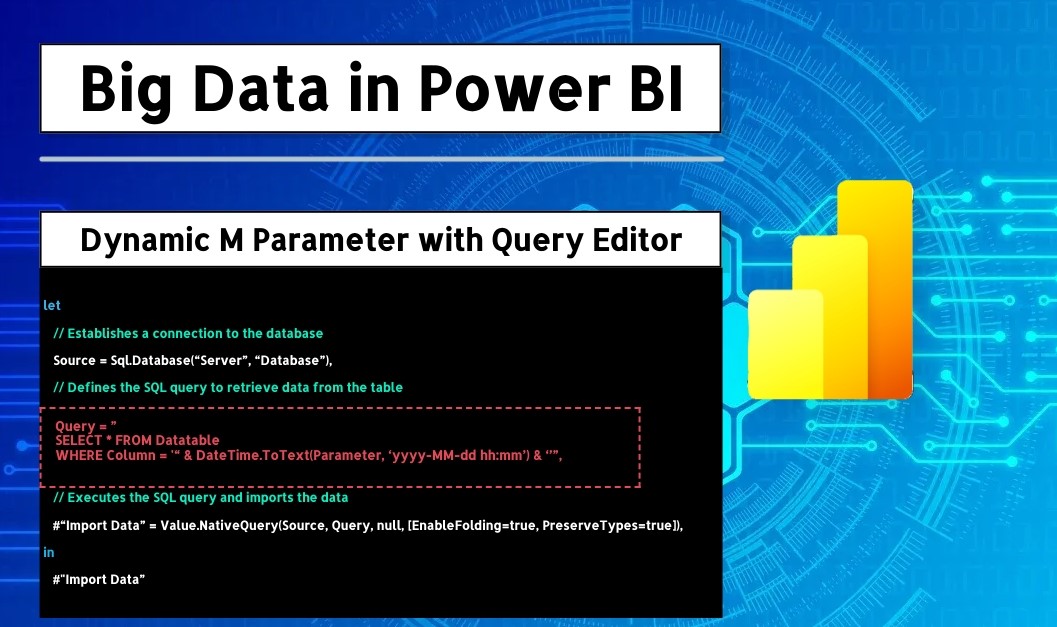
Below is an example of a dynamic M query that connects to a SQL database and retrieves only a subset of data based on a date parameter.
let
// Establishes a connection to the database
Source = Sql.Database("Server", "Database"),
// Defines the SQL query to retrieve data from the table
Query = "
SELECT * FROM Datatable
WHERE Column = '" & DateTime.ToText(Parameter, "yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm") & "'",
// Executes the SQL query and imports the data
#"Import Data" = Value.NativeQuery(Source, Query, null, [EnableFolding=true, PreserveTypes=true])
in
#"Import Data"In this example:
- Parameter: This represents a dynamic date parameter that filters the data. When users adjust the parameter in Power BI, it triggers a new SQL query with the selected date value, limiting the retrieved dataset accordingly.
- EnableFolding: Query folding is enabled to allow the SQL database to handle as much of the computation as possible, further enhancing performance.
Benefits of Using Dynamic M Query Parameters
- Efficient Data Filtering: Rather than loading millions of rows and filtering in Power BI, Dynamic M parameters allow you to filter data at the source, ensuring that only relevant subsets are imported. This drastically improves performance.
- Enhanced Query Performance: Querying only necessary data reduces processing time, and by leveraging query folding, Power BI can push the computation to the database, which is often optimized for large-scale operations.
- Better User Experience: Users can interact with large datasets without long wait times, as Power BI retrieves only the required data, making the experience faster and more seamless.
Setting Up Dynamic M Parameters in Power BI
To set up dynamic M parameters in Power BI, follow these steps:
- Create the Parameter:
- Go to Manage Parameters in Power BI and create a new parameter (e.g., a date parameter).
- Define the parameter type, such as date or numeric, depending on the requirement.
- Edit the Query with M Code:
- In Advanced Editor, modify the M query to incorporate the parameter, as shown in the example above. Make sure to use
Value.NativeQueryto define the custom SQL statement with dynamic parameters.
- In Advanced Editor, modify the M query to incorporate the parameter, as shown in the example above. Make sure to use
- Test and Optimize:
- Test the parameter by adjusting its value and observing how the data retrieval responds.
- Enable query folding for optimal performance whenever possible.
Practical Use Case: Analyzing Billions of Data Points
In my use case, analyzing a dataset of 8 billion data points required a solution that could manage high data volumes without compromising speed. Here’s how the combination of DirectQuery and dynamic M parameters helped:
- Subset Filtering by Date: By applying a date filter, I could quickly narrow down to data from specific time frames, allowing Power BI to retrieve manageable slices of data on demand.
- Responsive Visualizations: With only relevant data loaded, Power BI visualizations responded quickly, offering a seamless experience despite the dataset’s size.
- Optimized Database Queries: With query folding, the database handled the heavy lifting of filtering and aggregating data, allowing Power BI to act as a lightweight visualization layer.
Final Thoughts: Leveraging Power BI for Big Data
Power BI’s DirectQuery mode and Dynamic M Query Parameters provide an effective solution for handling massive datasets. For data professionals dealing with billions of records, these tools enable efficient data querying and visualization without overloading Power BI or compromising performance.
Whether you’re dealing with real-time streaming data, operational data analysis, or any big data scenario, Power BI’s capabilities continue to grow. With a bit of optimization, you can leverage Power BI to transform big data into actionable insights.
By implementing these techniques, you can unlock Power BI’s potential for big data and harness powerful analytics even at scale. Happy querying!